Papillomavirus infections are spreading around the world. HPV infection occurs regardless of age and sex, but the course of the disease and its development is unique in men and women.
For men, the papilloma virus can cause certain disturbances in their sex lives and cause related health problems.
The reasons
The human papillomavirus is so microscopic that it can enter the body through the tiniest cracks in the skin and mucous membranes.
In this regard, there are several possible cases of HPV infection, which are:
- Sexually transmitted. You can get an infection not only through casual intimate contact but also through oral contact. In gay men, HPV enters through anal contact through cracks in the skin and in the rectum. Damage to the mucous membranes during sex increases the risk of infection.
- The route of infection in the family. The virus can stay in a state to survive for a long time in a humid environment, so there is a high possibility of transmission in baths, saunas, through personal towels. Cases of infection in beauty salons are described, where the rules for disinfecting manicure sets and other tools have been ignored. The virus can be transmitted through instruments in the dental or operating room.
- From mother to child during childbirth.
Men who frequently change sexual partners are more likely to become HPV-positive.
It is believed that the younger a girl is, the more likely she is to have a papilloma virus infection in her body - most infections are found to occur between the ages of 25 and up. Virgins can also get HPV, because oral sex and other forms of sex are often done before traditional sex.
Unfortunately, barrier contraception, i. e. condoms, is not a 100% guarantee of preventing HPV infection. This is because this microorganism, due to its minimal size, easily penetrates through the holes of the pus. Naturally, condoms reduce the chance of a possible infection, but don't eliminate it completely.
Also keep in mind that microorganisms are found in certain amounts in saliva and, therefore, can be transmitted through kissing.
The risk of HPV infection may be increased in men with bad habits. The possibility of infection increases when the body's defenses are weakened, after prolonged treatment with antibiotics.
Symptom
The fact that he is a carrier of the papilloma virus, a man may not suspect until the vital activity of this microorganism is activated. The cause of this change is usually an impaired immune defense system activity.
Latent infection takes place over a period of two weeks to a year, in some cases significantly extended.
Activation of the virus leads to the fact that part of it accumulates in a certain place on the skin or on the mucous membranes. The accumulation and growth of papillomavirus alters the function of epithelial cells and this leads to a tumor-like process.
Papillomas can form on almost any part of our body, they are most often noticed in the armpits, on the face, neck and genitals. Sometimes the process of papilloma formation is accompanied by itching and burning.
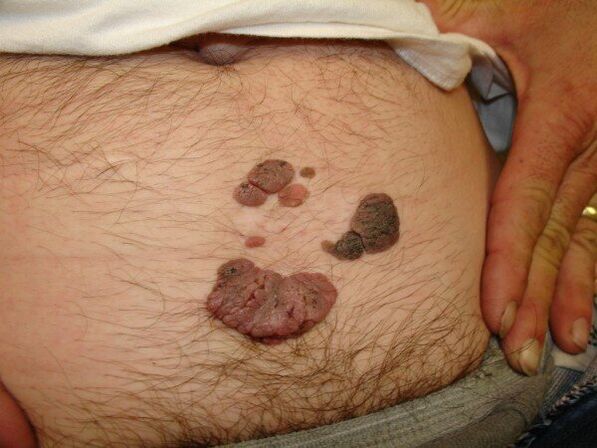
The papillomavirus formation on the body develops in the form of patches, warts, and bumps on the legs. The most dangerous are warts, in men they are located on the shaft of the penis, can grow around the anus or inside the urethra.
These growths often look like small pimples at first, in more severe cases they can fuse together, forming a cauliflower-shaped growth.
Genital warts themselves are only annoying because of a cosmetic defect. But if they are not removed and generally treated with the papilloma infection, there is a risk of degeneration of the epithelial cells that have changed into cancer cells.
Sometimes, during sex or careless movement, the papillomas are damaged resulting in slight bleeding and soreness. With the strengthening of the immune system, self-healing usually occurs, i. e. papillomas disappear or they become smaller.
Effect
The consequences of a male papillomavirus infection are unpleasant and dependent on the strain of the microorganism.
If the inside of the urethra is affected, warts inside the urethra are at risk of growing and spreading rapidly. This leads to partial or total obstruction, negatively affects the flow of urine and affects the development of disorders in the functioning of the urinary organs.
The presence of a tumor on the glans of the penis, around the anus, and in the rectum increases the likelihood of a benign formation becoming a malignancy.
Rectal cancer is often found in men who have had non-conventional sex. During oral sex, there is a risk of the formation of papillomas in the throat, manifested by various unpleasant sensations.
A man infected with HPV also poses a certain danger to women in his environment. For his wife or other sexual partner, such a man would be the highest source of infection. Sisters, mothers, aunts and sisters are all at risk of infection when using the same towels and bath accessories in the family.
diagnostic method

Establishing the diagnosis begins with an examination of the external genitalia and the patient's entire body.
It is imperative that the doctor collects a history, that is, to clarify when the formations appear on the body, what the patient associates their development with, and determine whether there are certain complaints. .
To confirm the diagnosis, the patient must pass several tests, which are:
- A swab or scrape from the inner lining of the urethra.
- PCR test to determine the virus type, quantitative content. This analysis is done after taking a smear, prostate secretions, or blood.
- Biopsy - a study of a tissue sample taken during removal of a genital wart or from a site of mucosal change.
- Ureteroscopy helps to visually examine changes in the urethra.
Men who have sex with men should examine swabs taken from the anal area.
Methods of treating papillomavirus in men
The choice of treatments for human papillomavirus in men depends on which strains of the virus are detected in the man.
If a pathogen with high carcinogenic activity is detected, then an effective antiviral treatment is indicated and in the future it is necessary to continuously repeat the tests.
Papillomas and foreskin are removed from the skin and mucous membranes in several ways. This can be conventional scalpel cutting or more modern methods - laser treatment, electrocautery, radio wave methods.
After removing the papilloma, it is necessary to increase the body's resistance to infections, which will reduce the risk of contracting another type of HPV.
Prevent
Prevention of human papillomavirus infection is evident during sex and, if possible, sex only with trusted partners. Prevention methods include following the basic rules of everyday life, that is, using only your own towels and underwear, following a healthy lifestyle.
Infections can be prevented by vaccination. A special vaccine has been developed against the HPV virus, which is given three times over a set period of time. Vaccination leads to the fact that the body develops immunity to certain strains of the papilloma virus.














































































